In Java world, classes are interrelated to each other in
specific ways. In particular, the relationships in classes have different types
of logical connections.
These logical connections /relationships among classes are
defined in UML in following ways:--
1. Association
2. Aggregation
3. Composition
4. Inheritance/specialization
5. Realization
6. Dependency
1. Association:
Association can be
defined as any logical connection or link or relationship between classes. For
example students study in school or a person works for a company.
Association is represented by a solid line between classes
as shown below:--
Association has
following properties:--
Name: Indicates the
name of the association. Here in above example, “works for” is the name of the
association.
Role: It indicates
the role played by each entity in the association. Here in above example,
person class plays the role of employee whereas Company plays the role of
employer.
Multiplicity: It
indicates how many objects of one class relate to one object of other class. Below diagram indicates that that 1 or more
person objects are associated with 1 company Object.
Direction: It indicates the direction of association. In
above example, association is from Person class where employee works for a
Company.
2. Aggregation:
It a specialized form of association where one object has reference
to another object but both objects has their own life cycles (independent to
each other).
Aggregation is also known as “HAS-A” relationship
because he containing object has a member object and the member object can survive or exist
without the enclosing or containing class or can have a meaning after the
lifetime of the enclosing object also.
For example: Room has
table and table can exist without room. Table has meaning without room also.
Aggregation can be represented as below:
Here Library has references to Books but instances of both
classes has independent life cycle. Books have some meaning even if library doesn't
exist. Books can still be there if library doesn't exist.
(Note: the direction of the diamond should be
towards the container class)
3. Composition:
Composition is a special case of aggregation where one
object contains other object but contained object can’t survive without
container object.
Composition
is also known as a 'is a part of' or 'is a' relationship because the member
object is a part of the
containing class and the
member object cannot survive or exist outside the enclosing or containing class
or doesn't have a meaning after the lifetime of the enclosing object.
If parent
object is deleted, all its children objects have to be deleted.
 Any department say Computer Science department is part of college.
The Computer Science Department cannot exist without the college and the department has no meaning after the
lifetime of the college.
Any department say Computer Science department is part of college.
The Computer Science Department cannot exist without the college and the department has no meaning after the
lifetime of the college.
4. Inheritance/Specialization:
Generalization refers to the inheritance relationship where
the attributes and behavior of the super (parent) class is inherited by the sub
(child) class.
Generalization in UML is denoted by solid line followed by a
triangular arrow. The arrow will be directed from the child class to the parent
class.Inheritance relationship is shown below:--
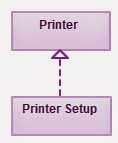
5. Realization:
Realization is relationship between a blue print class (Interface
in Java) and implementation class. It is
represented as a dotted line followed by a triangular arrow. For example:--
6. Dependency:
Dependency relationship between two entities is defined when
one entity is dependent on another. The entity which depends on another is
called the dependent entity and the other entity is called as independent
entity. When there are any changes in independent entity, then it may affect
the dependent entity, but the vice versa is not applicable.
It is represented as:-





No comments:
Post a Comment